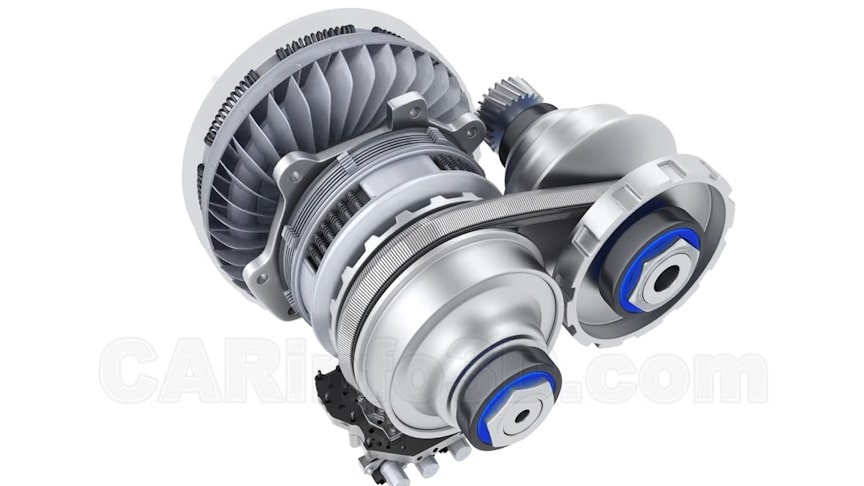
CVT Continuously variable transmission is a type of an automatic transmission that is commonly utilized in passenger cars. We will consider the structure and principle of operation of this gearbox on one example. A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automated transmission that can change through a continuous range of gear ratios, typically resulting in better fuel economy in gasoline applications.[1] This contrasts with other transmissions that provide a limited number of gear ratios in fixed steps.
source.image: CARinfo3d (En)
The flexibility of a CVT with suitable control may allow the engine to operate at a constant angular velocity while the vehicle moves at varying speeds. Thus, CVT has a simpler structure, longer internal component lifespan, and greater durability. Watch the 3D Animation from CARinfo3d (En):
CVTs are used in cars, tractors, side-by-sides, motor scooters, snowmobiles, bicycles, and earthmoving equipment. The most common type of CVT uses two pulleys connected by a belt or chain; however, several other designs have also been used at times. The most common type of CVT uses a V-belt which runs between two variable-diameter pulleys. The pulleys consist of two cone-shaped halves that move together and apart.
Advertisement
The V-belt runs between these two halves, so the effective diameter of the pulley is dependent on the distance between the two halves of the pulley. The V-shaped cross-section of the belt causes it to ride higher on one pulley and lower on the other; therefore, the gear ratio is adjusted by moving the two sheaves of one pulley closer together and the two sheaves of the other pulley farther apart.