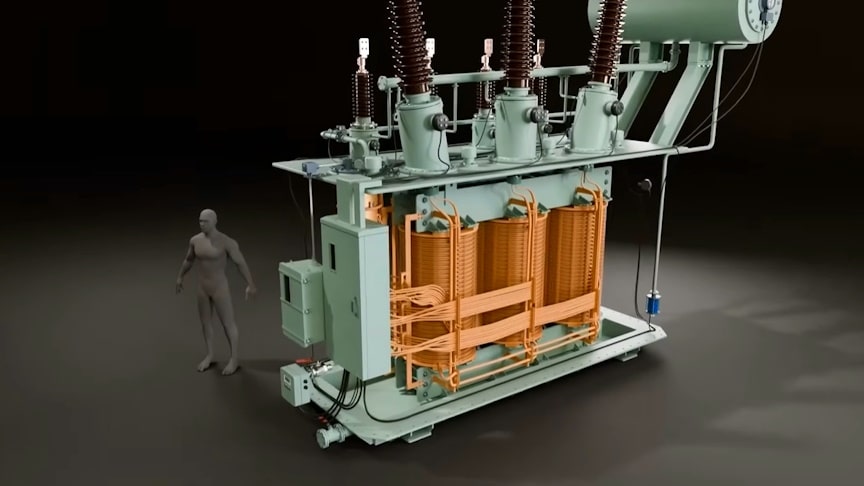
Power transformers are crucial for ensuring a steady and safe supply of electricity to homes and industries. They act as silent, behind-the-scenes heroes that step down high-voltage power for everyday use. The intricate technology within transformers efficiently converts and transports electricity across vast distances, ultimately powering our modern comforts and technologies seamlessly.
source.image: The science works
A basic transformer is made from two coils of wire; a primary coil from the ac input and a secondary coil leading to the ac output. The coils are not electrically connected. Instead, they are wound around an iron core. This is easily magnetised and can carry magnetic fields from the primary coil to the secondary coil.
Transformers change the voltage of the electrical signal coming out of the power plant, usually increasing (also known as “stepping up”) the voltage. Transformers also reduce (“step down”) the voltage in substations, and as distribution transformers. Transformers are also used as a part of devices, like current transformers. Transformers use electromagnetic induction to change the voltage and current. This change is called transformer action, and describes how the transformer changes an AC signal from its primary to its secondary component.
Advertisement
When an AC signal is applied to the primary coil, the changing current causes a magnetic field to change. This changing magnetic field will pass through to the secondary coil inducing a voltage across the secondary coil, thereby effectively coupling the AC input from the primary to secondary component of the transformer. The voltage applied to the primary component will also be present in the secondary component.