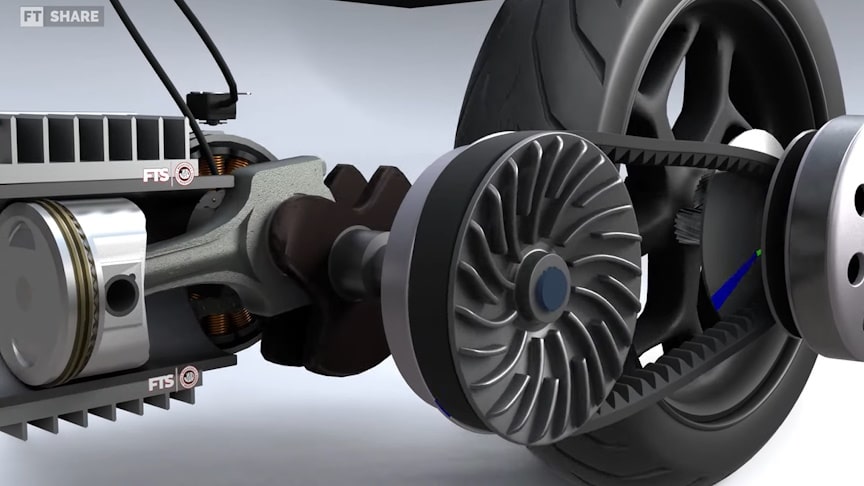
Most modern scooters use a continuously variable transmission (CVT), which differs from traditional manual or automatic transmissions. The transmission system in a scooter (often referred to as a “scooty”) plays a crucial role in converting the engine’s power into movement.
source.image: Ft-share International
A continuously variable transmission (CVT) is an automated transmission that can change through a continuous range of gear ratios. This contrasts with other transmissions that provide a limited number of gear ratios in fixed steps. video by Ft-share International:
The heart of the CVT system, consisting of two pulleys and a belt. The variator adjusts the diameter of the pulleys to change the gear ratio continuously. Primary Pulley: Connected to the engine, this pulley expands and contracts based on engine speed. Secondary Pulley: Connected to the rear wheel, this pulley also adjusts its diameter in response to the primary pulley.
Advertisement
Most scooters have a centrifugal clutch that engages the transmission when the engine reaches a certain RPM. This allows for smooth acceleration without manual input. The power from the secondary pulley is transmitted to the rear wheel, usually through a chain or a shaft.