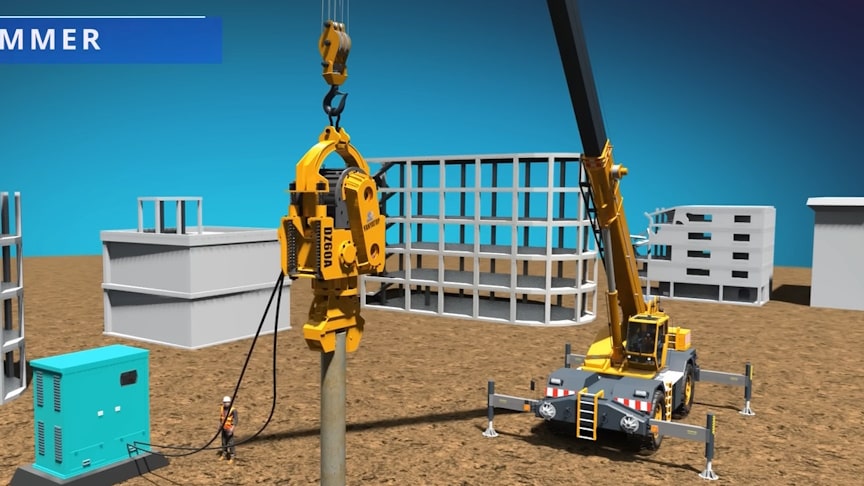
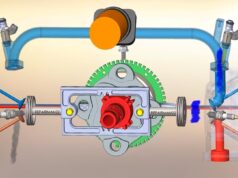
A vibratory hammer is a tool used to drive piles into the ground when building foundations for things like bridges, buildings, roads, marine docks, walls or railways. Vibratory hammers work by eliminating soil resistance acting on the pile. The vibrations generate pore pressures which reduce the effective stress in the soil and, therefore, the soil shear strength.
source.image: Sabins Civil Engineering
Avibratory hammer works more like an electric knife cutting through meat. Using a traditional pile driver, it might take up to an hour to drive a 100 foot pile into the ground, but with a vibratory hammer that same pile can be installed in about 10 minutes. When a hammer impacts on a pile head, the force, or stress, transferred to the pile builds progressively to a peak value and then decays to zero. Watch the video from Sabins Civil Engineering:
The entire event is over within a few hundreds of a second. During this time, the transfer initiates a compression strain wave that propagates down the pile at the speed of sound. At the pile toe, the wave is reflected back toward to the pile head.
Advertisement
There are two main styles of vibratory hammers: electric and hydraulic. These two styles share three main similarities: Both use a power unit to power the hammer. Both have clamps that allow the hammer to attach to the pile. Both use wires to connect the hammer to the power unit. Regular vibratory hammers can generate high levels of noise and vibration, which can be detrimental to nearby structures and ecosystems. I hope you enjoyed the physics behind vibro pile hammers.