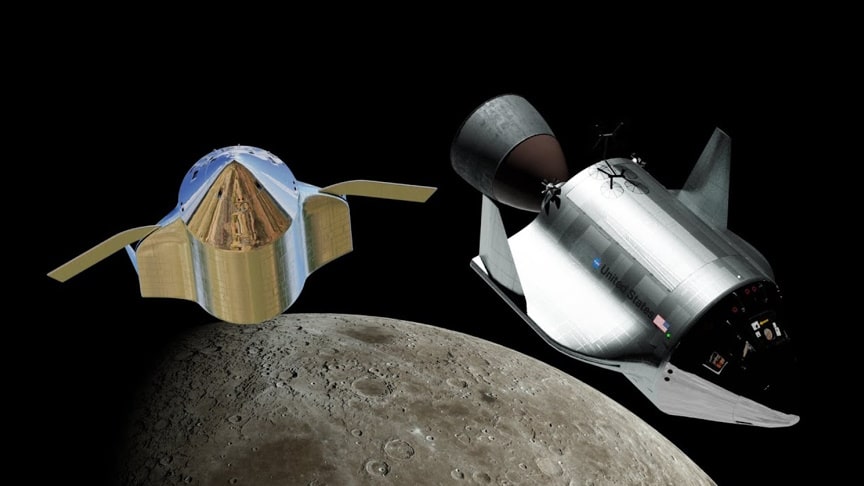
An aerospace vehicle is described comprising a substantially conical forward crew compartment or command module mated to a substantially cylindrical rearward service module. Aerodynamic fairings are provided along the midline on the sides of the cylindrical portion and a substantial distance aft thereof for providing lift at hypersonic velocities and approximately vertical fins are provided on the fairings for aerodynamic stability and control.
source/image: Hazegrayart
Wings are mounted within the aerodynamic fairings at high velocities and pivotably extended there from at lower velocities and altitudes to provide low speed lift. Upon reentry into the earth’s atmosphere hypersonic lift is provided by the body and the fairings for bringing the vehicle to the area of a selected landing site and, at lower flight speeds deeper into the atmosphere, augmented lift is provided by the extended wings for landing the vehicle on a conventional runway.
A rocket engine for propulsion has a large expansion ratio bell for use in the vacuum of space. The large ratio bell is jettisonable. Rear landing skids are pivotable into and out of the wake of the vehicle to reduce the requirement for heat shielding.
Advertisement
Similarly, reaction control rocket motors are also pivotable into and out of the wake of the vehicle for minimizing heat protection requirements. uch a vehicle is readily adaptable to a broad variety of space missions such as cargo ferry or satellite recovery, and is reusable with minimum refurbishment.United States Patent 3,576,298 applied for in 1967 and issued to the North American Rockwell Corp in 1971.via: Hazegrayart