In electrical engineering, ground or earth is a reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured, a common return path for electric current, or a direct physical connection to the earth.
source/image(PrtSc): The Engineering Mindset
Electrical circuits may be connected to ground for several reasons. Exposed conductive parts of electrical equipment are connected to ground, to protect users from electrical shock hazard. If internal insulation fails, dangerous voltages may appear on the exposed conductive parts.
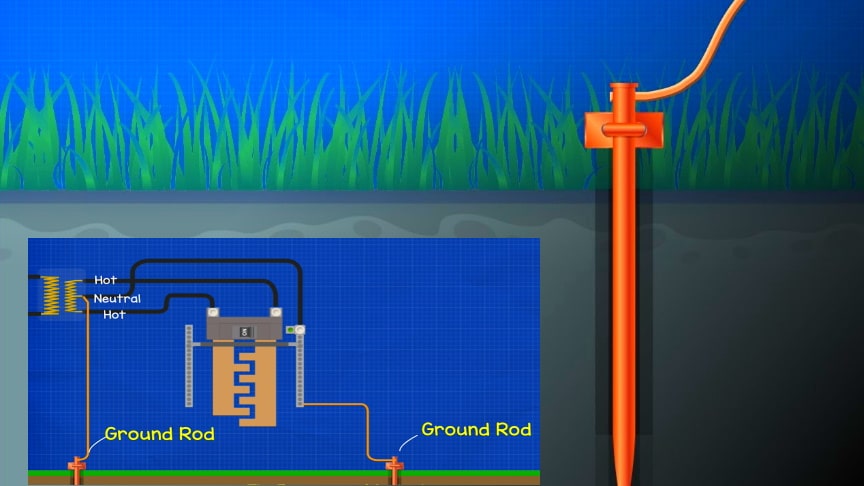
By connecting exposed parts to ground, little or no voltage will be present. The ground connection will allow over-current protection in the circuit to interrupt power supply.A ground rod is usually located very close to your main electrical service panel and is often made of copper or copper coated steel.
Advertisement
They’re approximately ½” in diameter and eight to 10 feet in length. It must be electrically tied to your main service panel to provide an approved ground connection.If a single ground has a resistance of 25 ohms or less, building codes allow it to be used as the only grounding device. If the resistance of a ground rod is greater than 25 ohms, at least one additional ground rod is required./The Engineering Mindset