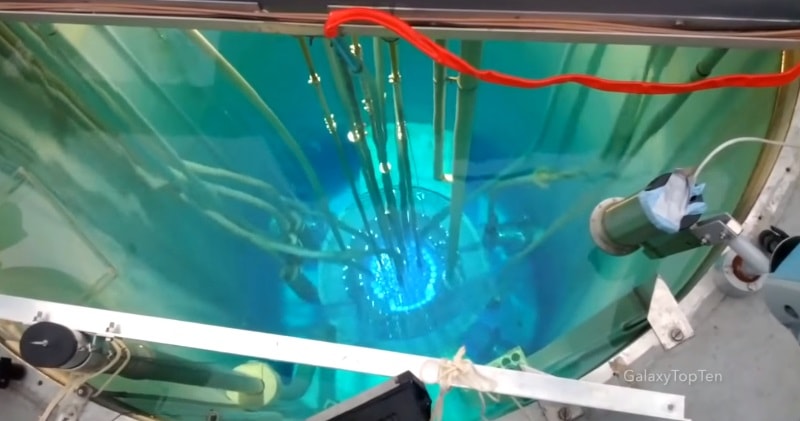
The blue light is known as Cherenkov radiation. It is similar to a sonic boom, but instead of an object travelling faster than the speed of sound, a charged particle is travelling faster than the speed of light in a medium. In this case, the speed of light in water is roughly 75% the speed of light in a vacuum.
image/text credit: GalaxyTopTen
It tests the time-dependent properties of the fuel. Engineers use that data to predict what would happen if there were an accident at a large reactor.
Cherenkov radiation, also known as Vavilov–Cherenkov radiation, is electromagnetic radiation emitted when a charged particle (such as an electron) passes through a dielectric medium at a speed greater than the phase velocity of light in that medium.
Advertisement
The characteristic blue glow of an underwater nuclear reactor is due to Cherenkov radiation.Essentially when light passes through different materials its speed can be slowed as the photon makes it way through the medium.