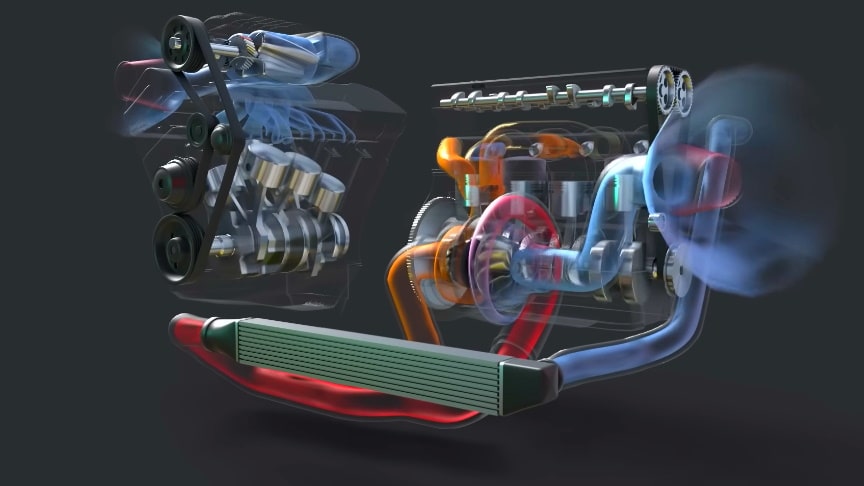
In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger (often called a turbo) is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gasses. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.
source/image: Animagraffs
In an internal combustion engine, a supercharger compresses the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement. Watch the video from Animagraffs for more info:
Turbochargers use the vehicle’s exhaust gas; two fans – a turbine fan and a compressor fan – rotate from exhaust gas. Conversely, superchargers are powered directly by the engine; a belt pulley drives gears that cause a compressor fan to rotate.
Advertisement
Supercharger also pumps additional air into the engine, but it is instead driven mechanically by the engine via a belt that runs off the crankshaft or by an electric motor.Supercharged engines are common in applications where throttle response is a key concern, and supercharged engines are less likely to heat soak the intake air./wikipedia