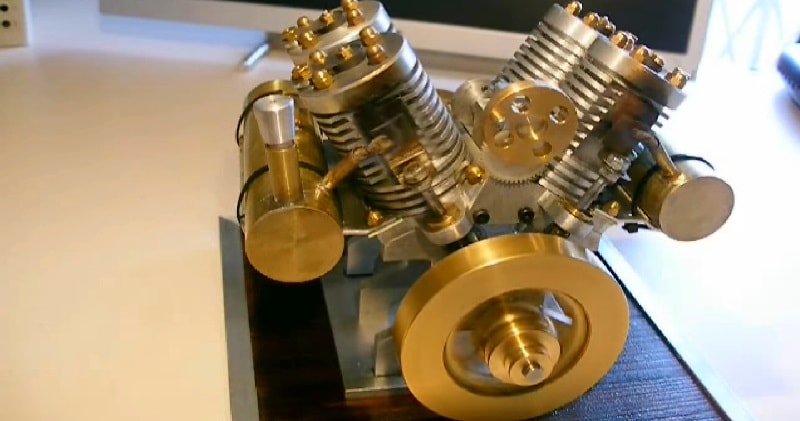
A vacuum engine also called flame-licker engine, flame-engine, flame-dancer derives its force from air pressure against one side of the piston, which has a partial vacuum on the other side of it.
source/image: Josep Mª Font
At the beginning of an outstroke, a valve in the head of the cylinder opens and admits a charge of burning gas and air, which is trapped by the closing of the valve and expands./wikipedia
Towards the end of the stroke the charge comes into contact with a water- or air-cooled part of the cylinder and is chilled.Causing a sudden drop in pressure sufficient to suck the piston – which is open towards the crank – back on the return stroke.
Advertisement
The valve opens again in time for the piston to expel the burnt gases before the next outstroke begins.A small amount of fuel and a constant burning flame can work this amazing engine.