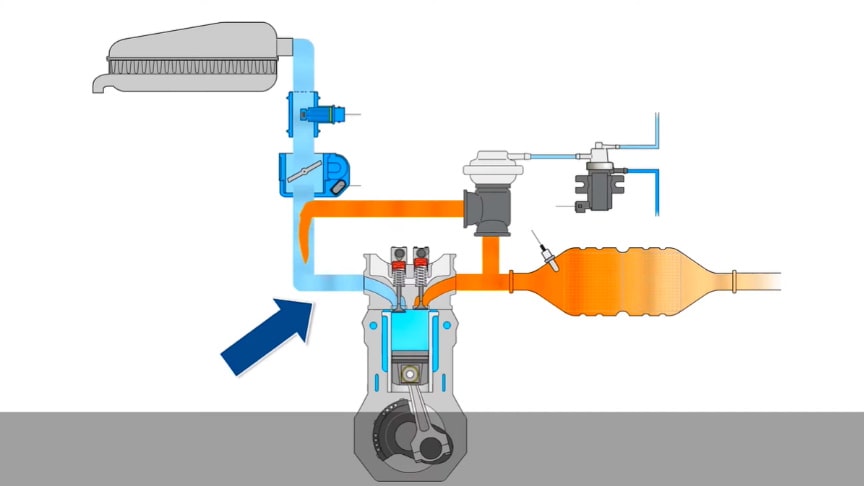
In internal combustion engines, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) is a nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions reduction technique used in petrol/gasoline, diesel engines and some hydrogen engines. EGR works by recirculating a portion of an engine’s exhaust gas back to the engine cylinders.
source/image(PrtSc): Motorservice Group
This dilutes the O2 in the incoming air stream and provides gases inert to combustion to act as absorbents of combustion heat to reduce peak in-cylinder temperatures. NOx is produced in high temperature mixtures of atmospheric nitrogen and oxygen that occur in the combustion cylinder, and this usually occurs at cylinder peak pressure.
Exhaust gas recirculation is used to reduce harmful emissions from petrol and diesel engines. In this video, we show you how EGR operates, the components it is made up of and how they work.
Advertisement
Another primary benefit of external EGR valves on a spark ignition engine is an increase in efficiency, as charge dilution allows a larger throttle position and reduces associated pumping losses.In a typical automotive spark-ignited (SI) engine, 5% to 15% of the exhaust gas is routed back to the intake as EGR. The maximum quantity is limited by the need of the mixture to sustain a continuous flame front during the combustion event; excessive EGR in poorly set up applications can cause misfires and partial burns./wikipedia