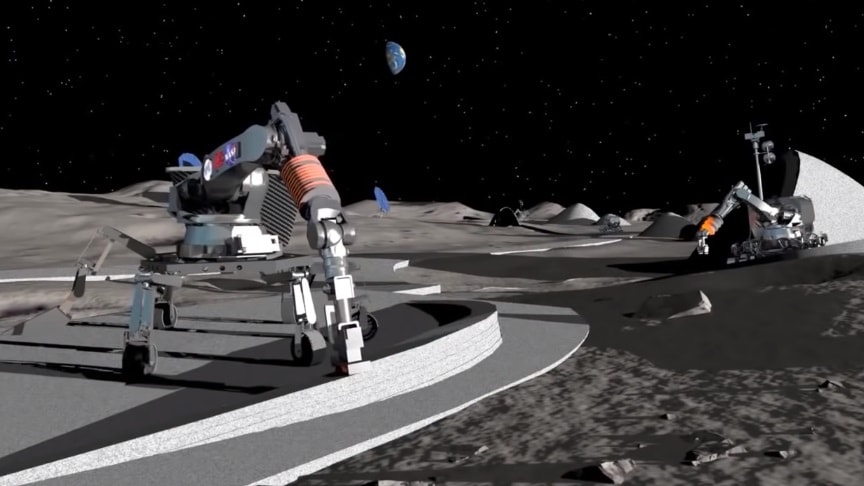
ESA has awarded the study “Conceiving a Lunar Base Using 3D Printing Technologies” to the URBAN Consortium comprising of COMEX, LIQUIFER Systems Group and SONACA Space GmbH under the lead of OHB System AG.
The team evaluated the feasibility and implementation effort of using Additive Layer Manufacturing in the construction, operations and maintenance of a lunar base.Everything from building materials to solar panels, equipment and tools to clothes, even nutrients and food ingredients can potentially be 3D printed.
Maximised 3D printing would also allow on-demand production of items and spares with routine recycling of materials available within the base, making lunar settlement much more self-sufficient and sustainable.
Advertisement
In space, energy typically comes via solar panels that provide almost instantaneous electricity when the Sun shines on them. But inhabitants of the Moon could expect to spend up to 16 days in darkness during the lunar night. Finding a sustainable energy solution that collects sunlight during the long lunar days and stores it for use at night is essential to make the prospect of long-term lunar habitation a reality.